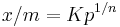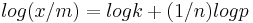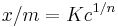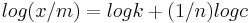Freundlich equation
The Freundlich equation or Freundlich adsorption isotherm is an adsorption isotherm, which is a curve relating the concentration of a solute on the surface of an adsorbent, to the concentration of the solute in the liquid with which it is in contact. In 1909, Freundlich gave an empirical expression representing the isothermal variation of Adsorption of a quantity of gas adsorbed by unit mass of solid adsorbent with pressure. This equation is known as Freundlich Adsorption Isotherm or Freundlich Adsorption equation. There are basically two well established types of adsorption isotherm: the Freundlich adsorption isotherm and the Langmuir adsorption isotherm. Here the amount of mass that is adsorbed is plotted against the temperature which gives an idea about the variation of adsorption with temperature.
Freundlich adsorption isotherm
The Freundlich Adsorption Isotherm is mathematically expressed as
It is also written as
or
It is also written as
where
- x = mass of adsorbate
- m = mass of adsorbent
- p = Equilibrium pressure of adsorbate
- c = Equilibrium concentration of adsorbate in solution.
K and n are constants for a given adsorbate and adsorbent at a particular temperature.
At high pressure 1/n = 0 Hence extent of adsorption is independent of pressure
But at high pressure it is dependent on pressure
Limitation of Freundlich adsorption isotherm
Experimentally it was determined that extent of adsorption varies directly with pressure till saturation pressure Ps is reached. Beyond that point rate of adsorption saturates even after applying higher pressure. Thus Freundlich Adsorption Isotherm failed at higher pressure.
References
Adsorption on heterogeneous surfaces: the exponential equation for the overall adsorption isothermM Jaroniec - Surface Science, 1975 Elsevier Binary Langmuir and Freundlich isotherms for ideal adsorbed solutionsMD LeVan… - The Journal of Physical Chemistry, 1981 - ACS Publications
External links
- http://www.rpi.edu/dept/chem-eng/Biotech-Environ/Adsorb/equation.htm
- http://www.xamplified.com/freundlich-adsorption-isotherm/
|
|||||||||||||||||